From Welding Robots to Writing Bots: How AI Advances the Automation Revolution
The first robotic welders sparked an automation revolution in manufacturing. Now, AI is igniting the next wave - dramatically reducing the cost of automating knowledge workflows.
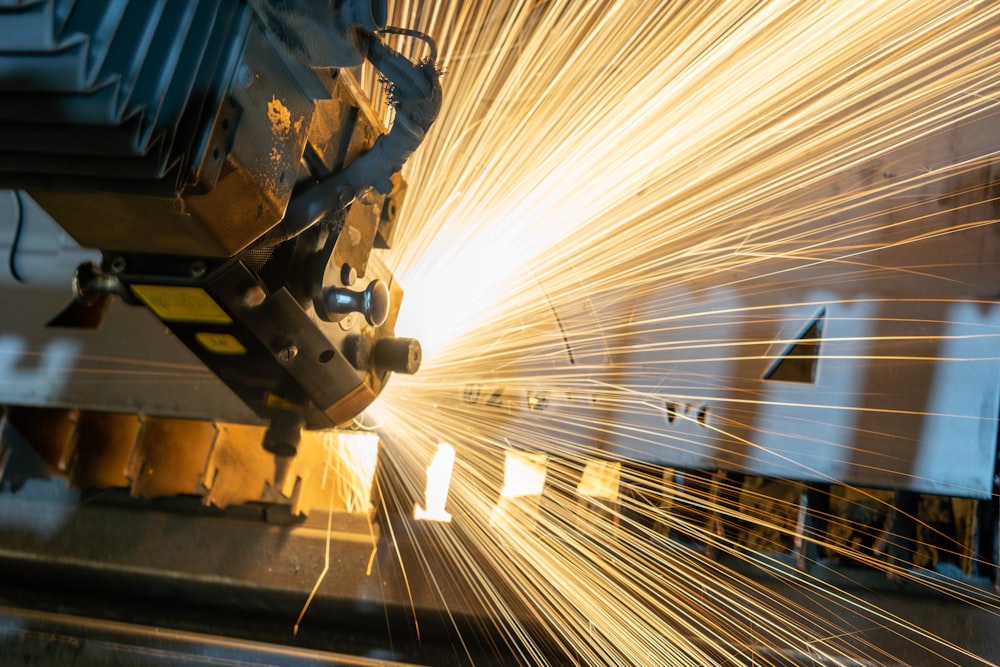
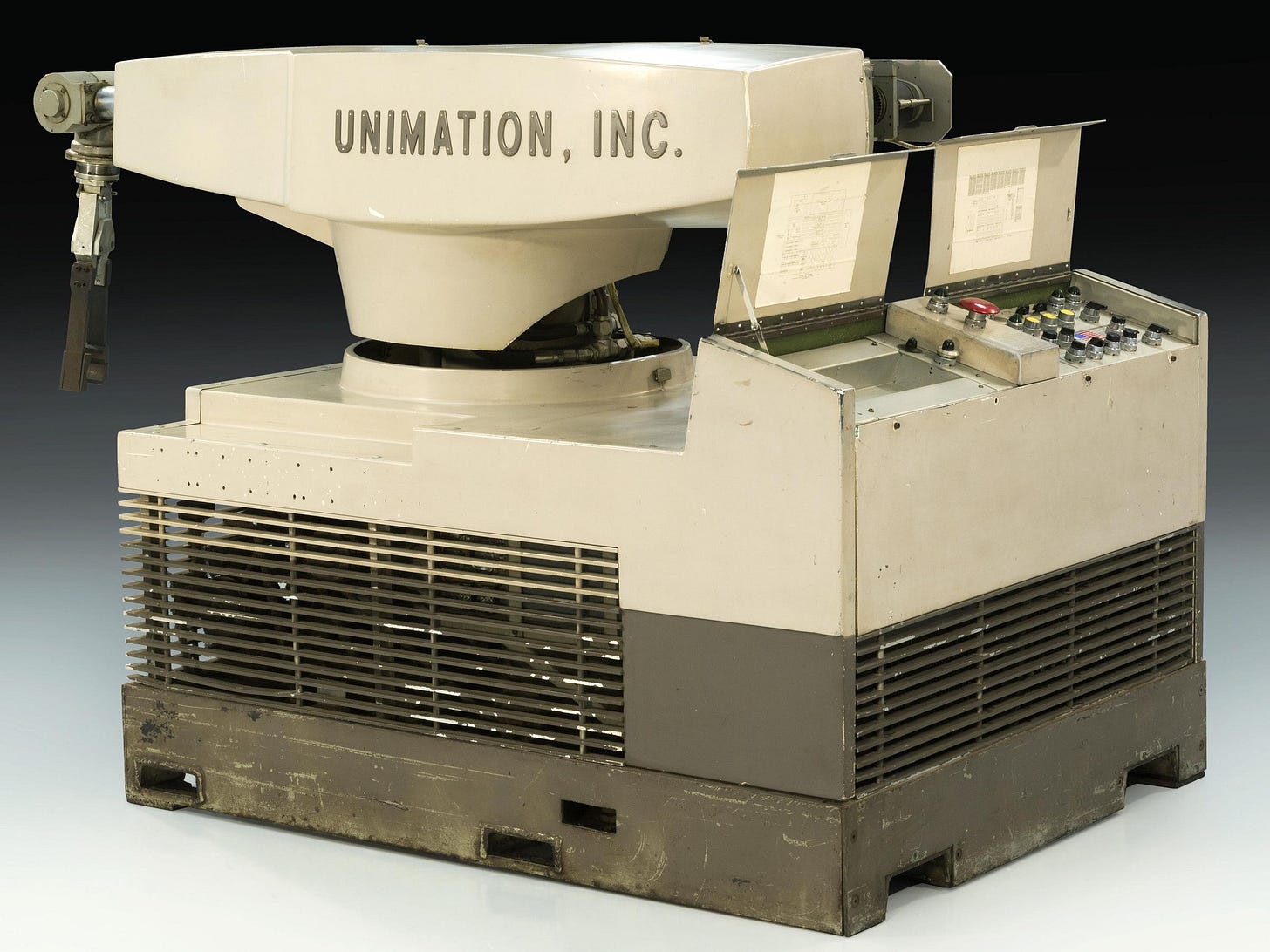
The year was 1961. Inside the noisy General Motors plant, sparks flew as workers moved in choreographed unison, wielding welding torches to piece together car bodies by hand. This "metal ballet" was standard practice - until that day when a hulking robotic arm was wheeled onto the floor. Known as Unimate, this was the world's first industrial welding robot, developed by pioneers George Devol and Joseph Engelberger. As Unimate began precisely welding auto parts together, the team watched anxiously, hoping their bet on this new technology would pay off. It did - that moment marked the start of a robotic revolution that would transform manufacturing forever.
Rise of the Robotic Welders
Unimate's success at General Motors opened the floodgates for robotic welding in auto manufacturing. Robotic arms boosted production speed and efficiency by taking over the dangerous job humans once did manually. Defects plummeted as precision-programmed robots made consistently high-quality welds. Robotic welding exploded in popularity throughout the 1960s and 70s as auto plants rushed to automate production. By the 1980s, GM's rivals like Ford and Chrysler were urgently playing catch-up in adopting the technology. Robotic welding has evolved to use advanced sensors, computer vision, and AI to adapt to changing conditions. This advancement has superseded manual welding on an overwhelming scale, with over 60,000 robotic welding cells deployed throughout North America.
The journey from physical to digital assembly lines
Assembly lines exist to coordinate complex, multi-step processes. Whether constructing cars or crafting blog posts, assembly lines enable many specialists to refine the product in sequence.
Consider what goes into publishing a quality blog post. First, SEO strategists research keywords and topics. Writers draft the post, which then goes through multiple rounds of editing. Lawyers review for any compliance issues, and growth specialists optimize formatting and images before finally publishing.
PS: I’ve covered this before in this article:
This workflow mirrors an auto assembly line, where a chassis passes from station to station as workers install tires, electronics, seats, and so on. The end result is the same - a polished final product. Automating repetitive SEO analysis and social media posting brings efficiencies, just as robotic welders accelerated physical manufacturing lines
As information work has exploded, software to automate the digital assembly line has turned into a $583 billion industry.
Analyzing the Automation Potential of Automation
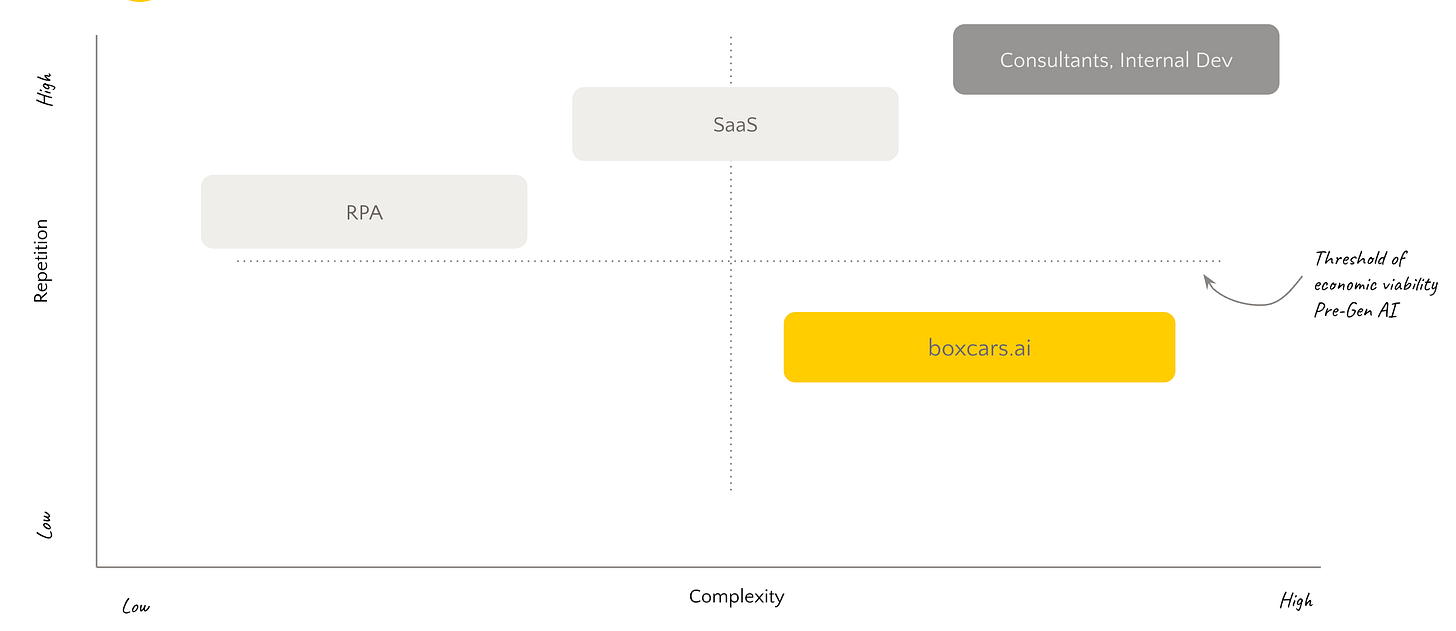
So, what is a good opportunity for an automation project? Let's consider a 2x2 matrix. The x-axis denotes task complexity from low to high. The y-axis covers repetition from low to high volume.
The Quick Wins: Low Complexity + High Repetition
This quadrant contains repetitive, straightforward tasks like copy-pasting data between systems. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) excels at automating high-volume, mundane tasks. Bots can rapidly complete simple actions like data entry far faster than humans and with tireless consistency.
As complexity increases, one-off scripts and tools give way to specialized SaaS apps. The SaaS industry thrives on highly specific applications, each aimed at slicing away small sections of larger workflows. Using the example of a blog post assembly line, specialized tools exist just to automatically post content to social media.
The Game Changers: High Complexity + High Repetition
This quadrant contains complex, repetitive tasks that have historically required custom solutions to automate. Specialized technical teams or consulting firms have built complex systems to automate high-value workflows.
For example, Google pioneered an automated ad auction platform. This revolutionary system leveraged algorithms to match buyers and sellers in real-time, replacing inefficient static sponsorships. Automating this complex process fueled online advertising's meteoric rise.
Other transformative automation achievements include personalized social media feeds and real-time fraud detection. However, these complex solutions were prohibitively expensive, and reserved only for high-volume tasks with substantial payoffs.
Automating Beyond the Threshold: Generative AI and the New Economics of Task Automation
Low repetition tasks have typically fallen outside automation's reach - the juice wasn't worth the squeeze. Why invest in an expensive consultant when human labor was affordable enough? But generative AI may alter the calculus.
Last week we covered how adapting fracking to shale formations was a game-changer, transforming the US from a potential importer to the top oil producer. Fracking made shale oil economically viable. Similarly, generative AI can now make automating previously uneconomical tasks viable.
Making the Simple Trivial and the Difficult Possible
The first way generative AI enables this transformation is by taking tasks that were straightforward but required some programming and making them trivial. If you were a developer, reformatting text into a CSV used to take an afternoon of mucking around with regular expressions and parsers. Now it's a simple right-click with an LLM, a good Chrome extension, and anyone can do it.
But what about more advanced analysis? Sentiment detection on customer feedback was tractable using machine learning models but required a ML team. Now it's within reach on a much lower budget. AI is starting to "frack" knowledge work, opening up new veins of automation.
This transformation is not limited to simple and repetitive tasks. Generative AI also accelerates existing high-end automation efforts, making them faster and more affordable. But the seismic impact is in democratizing automation for organizations and use cases where it was previously inaccessible.
Much like mobile phones allowed billions affordable access to the internet in a way desktops and laptops did not, AI is opening new frontiers of automated potential for businesses of all sizes.
At boxcars.ai, our focus is on democratizing access to automation powered by generative AI. We believe LLMs are enabling companies to acquire their own "robotic welders" - automating workflows once thought out of reach.
The future is here. Early adopters who harness this transformation, like GM with the first robotic welder, will see incredible productivity gains. If you have the vision to lead the pack, now is the time to explore how generative AI can revolutionize your workflows. Reach out, and let's chat about becoming an automation front-runner today. You can book time on my calendar here.